In the laboratory, different activities are carried out within the framework of university functions: research, extension and teaching, providing academic support to students who so request, in order to participate jointly in the formative processes of the academic courses in the School.
The Digital Integration Center (CID), through the LabFab-MVD, integrates a suitable human team for the training of the personnel in charge of the administration and operation of the equipment.
FabLab Montevideo provides support to the students in two different modalities, prioritizing the modality of “project monitoring” as a way of tutoring with digital fabrication with FabLab teachers, for students who wish to investigate the possibilities of digital fabrication applied to their project or prototype. On the other hand, students without project follow-up have the possibility of accessing the technology of the laboratory prior to reservation via email agenda.
The Digital Integration Center (CID), through LabFab-MVD, integrates a suitable human team for the fulfillment of the aforementioned tasks, carrying out the initial implementation of the necessary equipment for these purposes and the training of the personnel in charge of the administration and operation of the equipment.
> EQUIPMENT
3D Printing

Ultimaker
Printing areas
Raise3D Pro2 Plus, printing area: 300mm x 300mm and with max. height of 600mm.
Material
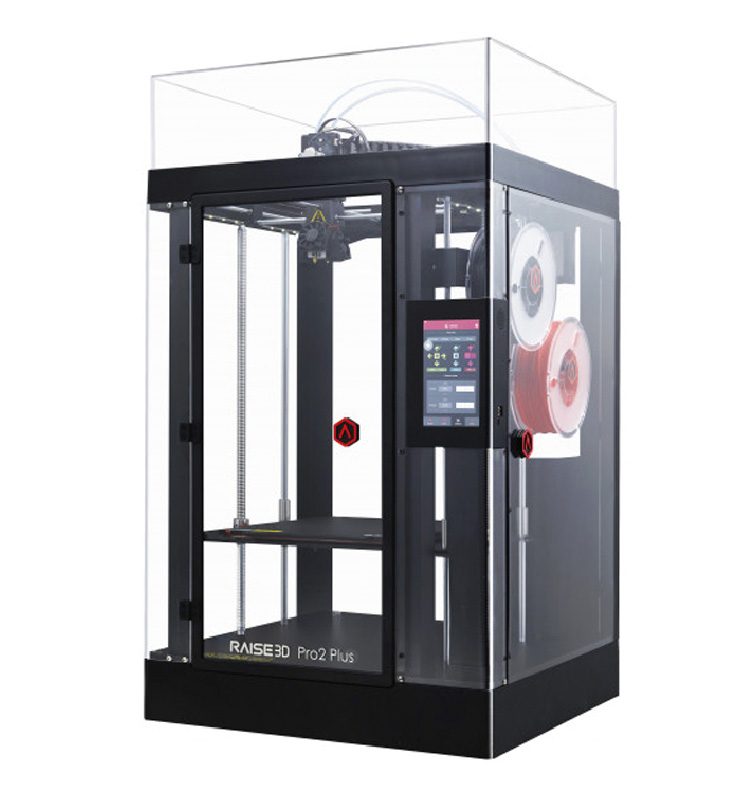

Raise3D Pro2 Plus
Laser cutter
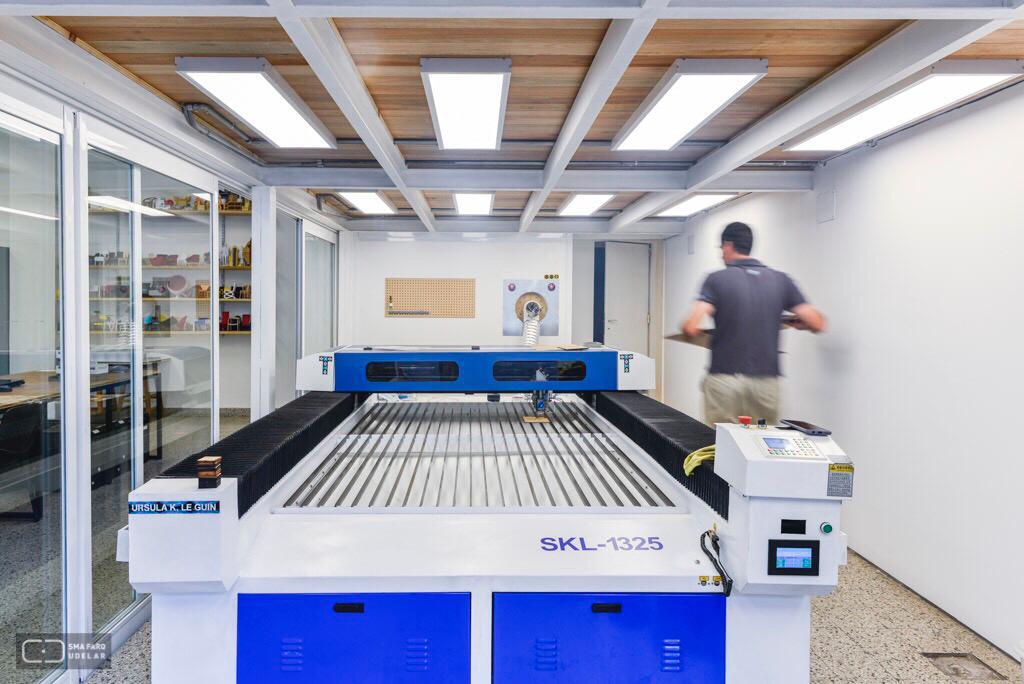

Senke, model: SKL-1325
Cutting area
Material
Material thickness
CNC cutter
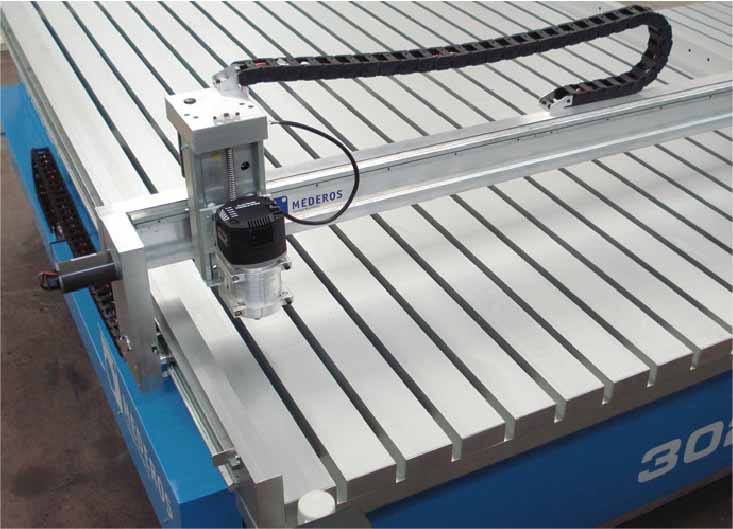

Router MEDEROS
Cutting area
Material
Material thickness
> PROTOCOLS AND FORMS
To schedule a day and time, it is essential to go to the laboratory (FabLab- MVD) with the file to work on, preferably between 9 a.m. and 10:30 a.m., or via email to labfab@fadu.edu.uy with an explanation of the project and the technology to be used, otherwise no job can be scheduled.
> FURTHER INFORMATION
Subtractive technologies
Laser cutting, router CNC, EDM machining and water jet cutting.
Subtractive fabrication is a generic term used to name various fabrication processes based on the use of CNC tools that allow digital designs to be materialized by removing material through cutting, drilling and grinding.
A laser cutter is a particular type of CNC machine. There are several…
Read more…
3D Printing:
Parameters and strategies
Additive manufacturing technologies are those used to convert digital models into three-dimensional objects, basing their construction on the deposition -that is, adding- material in successive layers.
We can use any 3D modeling software to generate the models, as long as there is the possibility of exporting it as an .STL (Stereo Lithography) file.

Digital Fabrication:
Aditive and sustractive fabrication
This type of manufacturing allows the processes to be repeatable as many times as necessary. In turn, the complexity of the object does not have a significant impact on the cost of production.